Choosing the wrong diaphragm material[^1] leads to valve failure and costly downtime. A bad choice means leaks and operational chaos. Understanding EPDM[^2] vs. PTFE[^3] is key to getting it right.
For water-based or non-corrosive media in mild conditions, choose EPDM[^2] for its flexibility and value. For aggressive chemicals, high-purity systems, or harsh environments, PTFE[^3] is the superior choice due to its excellent chemical resistance and durability. It's all about matching the material to the media.

I've seen clients struggle with this decision time and again. A simple choice can make or break an entire system's reliability. It seems straightforward, but the details really matter when you are dealing with industrial applications. So, let's break down exactly when you should be looking at EPDM[^2].
When Should You Choose an EPDM[^2] Diaphragm for Your Valve?
Need a durable diaphragm for a water or non-corrosive system without overspending? Choosing the wrong material can waste your budget. EPDM[^2] provides a reliable, cost-effective solution for these applications.
Choose EPDM[^2] for applications involving water-based fluids, mild chemicals, or abrasive slurries[^4] in moderate conditions. Its excellent flexibility and wear resistance make it ideal for power plants, wastewater treatment, and general industrial use where extreme chemical corrosion is not a primary concern.
I often tell clients in the water treatment and power generation sectors that EPDM[^2] is the workhorse of our industry. Its main advantage is its excellent flexibility. This ensures a tight, leak-proof seal cycle after cycle, even with slurries. It pairs perfectly with our cast iron and ductile iron valve bodies.
EPDM[^2] Application Checklist
When we recommend an EPDM[^2] diaphragm, we look at key factors. It excels in systems handling water, many salt solutions, and dilute acids or alkalis. It is not the right choice for oils or solvents, but for its intended use, it is incredibly durable.
Here’s a quick guide to its suitability:
| Application Area | EPDM[^2] Suitability | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Wastewater Treatment | Excellent | Resists abrasion from sludge |
| Power Plant Water | Excellent | Handles raw and treated water |
| Mining (Slurries) | Good | High flexibility and wear resistance |
| Chemical (Mild) | Good | Cost-effective for non-aggressive media |
Choosing EPDM[^2] in these cases means you get reliable performance without paying for chemical resistance you simply do not need.
When is a PTFE[^3] Diaphragm the Better Choice for a Pneumatic Valve?
Handling aggressive chemicals that destroyed your last diaphragm? A valve failure can shut down your line, costing you time and money. PTFE[^3] offers the superior chemical resistance you need.
Use a PTFE[^3] diaphragm in pneumatic valves[^5] for harsh applications involving corrosive chemicals, high-purity media, or high temperatures. Its near-universal chemical inertness and durability ensure long-term reliability and prevent contamination, making it essential for chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and other demanding industries.
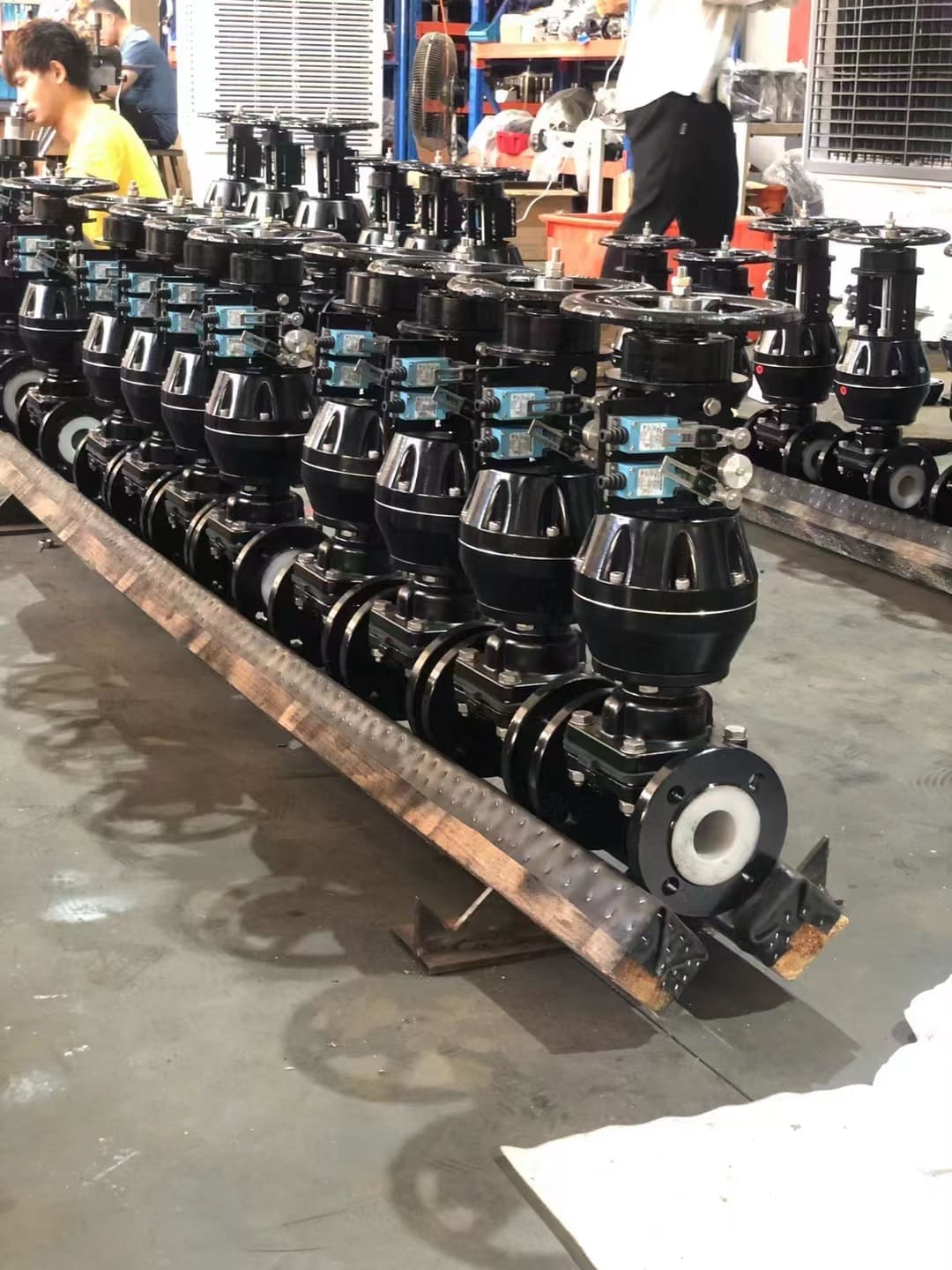

A client from a chemical plant was struggling with constant diaphragm replacements in their automated dosing system. Their pneumatic valves[^5] were failing every few months. Once they described the media—a mix of concentrated acids—I knew the issue. We switched them to our PTFE[^3]-lined valves, and the problem was solved.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE[^3] is nearly chemically inert. This means it will not react with or degrade when exposed to almost any industrial chemical. This is critical in automated systems where you need predictable, long-lasting performance without surprise failures.
The Purity Advantage
The non-stick surface of PTFE[^3] is also vital where media purity is essential. Contamination from the diaphragm material[^1] is unacceptable in high-purity applications. While EPDM[^2] is a great generalist, PTFE[^3] is the specialist for these critical tasks. It ensures your process runs cleanly and reliably, which is exactly what you want from a high-performance pneumatic valve.
Can Pneumatic Actuators Work Well With Both EPDM[^2] and PTFE[^3]?
Worried your actuator choice will limit your diaphragm options? A wrong assumption can cause poor performance and costly redesigns. Our pneumatic actuators work perfectly with both EPDM[^2] and PTFE[^3].
Yes, pneumatic actuators for diaphragm valves function efficiently with both EPDM[^2] and PTFE[^3] materials. The actuator's performance is not dependent on the diaphragm material[^1] but on providing the correct force. The choice of EPDM[^2] or PTFE[^3] is based entirely on the media's compatibility and process requirements.
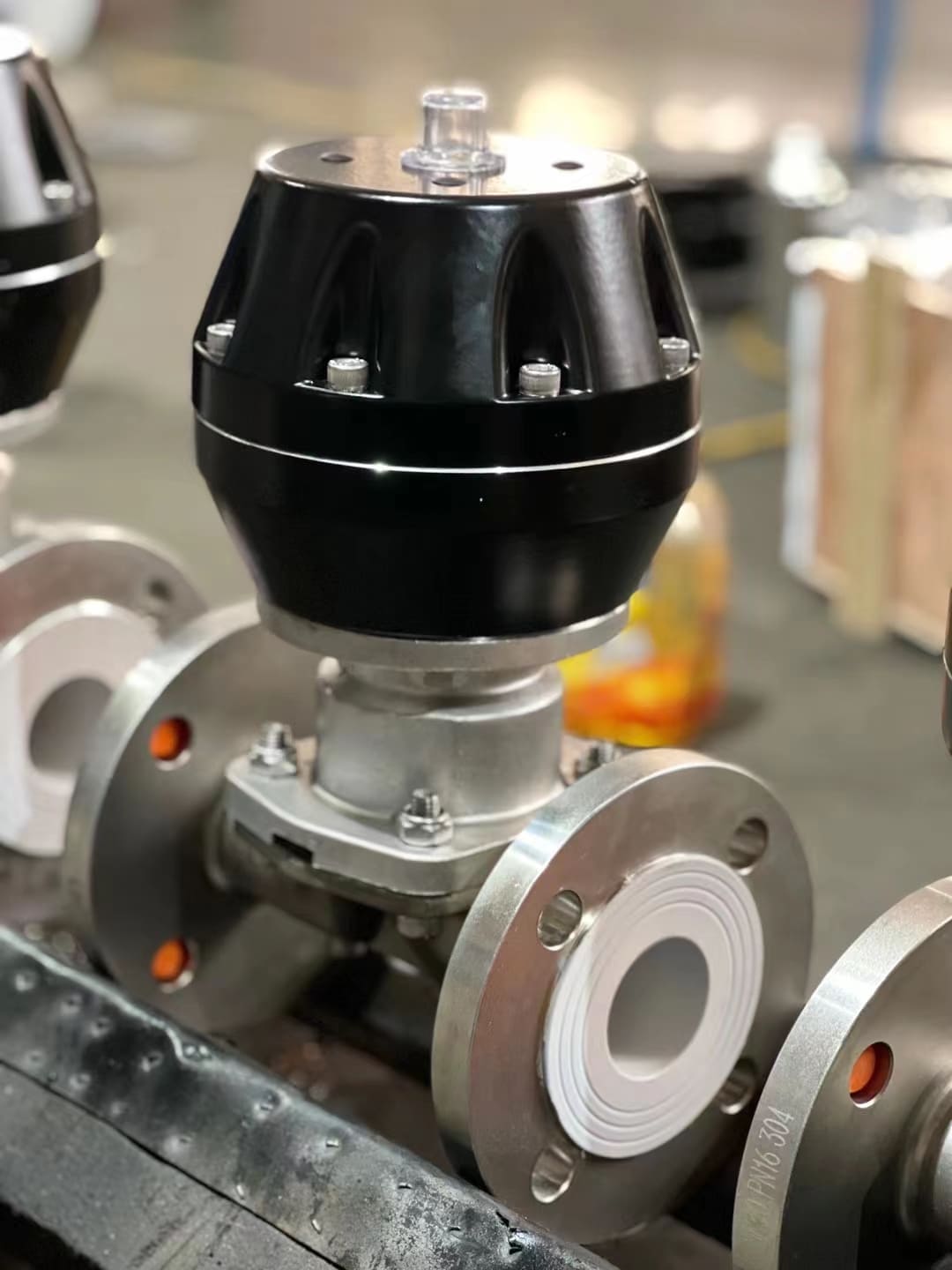

I often get asked if the diaphragm material[^1] affects the actuator. The simple answer is no. The actuator and the diaphragm have two distinct but complementary jobs, and our valve designs ensure they work together perfectly.
The Actuator's Role: Delivering Force
Think of the pneumatic actuator as the muscle. Its job is to provide a controlled force to close the valve against line pressure. It is sized to provide enough power, whether it is pushing on the highly flexible EPDM[^2] or a PTFE[^3] diaphragm.
The Diaphragm's Role: Sealing and Protecting
The diaphragm is the shield. Its job is to flex and create a tight seal, while also isolating the process media from the rest of the valve. The material choice is all about chemical compatibility.
| Component | Function | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Actuator | Provides Force | Sizing for line pressure |
| Diaphragm | Creates Seal | Material for media type |
This means you can confidently use our pneumatic actuators, knowing you can choose the best diaphragm—EPDM[^2] or PTFE[^3]—for your specific application.
Conclusion
In short, choose EPDM[^2] for general-purpose applications and PTFE[^3] for corrosive or high-purity media. Making the right material choice is the key to your diaphragm valve's performance and longevity.
[^1]: Explore this link to understand the importance of diaphragm materials in valve performance and reliability. [^2]: Learn why EPDM is favored for water-based applications and its advantages in flexibility and cost. [^3]: Discover the unmatched chemical resistance of PTFE and its applications in harsh environments. [^4]: Discover the challenges of using diaphragm materials in abrasive slurry applications and the best choices. [^5]: Explore the role of pneumatic valves in industrial applications and how diaphragm materials affect performance.